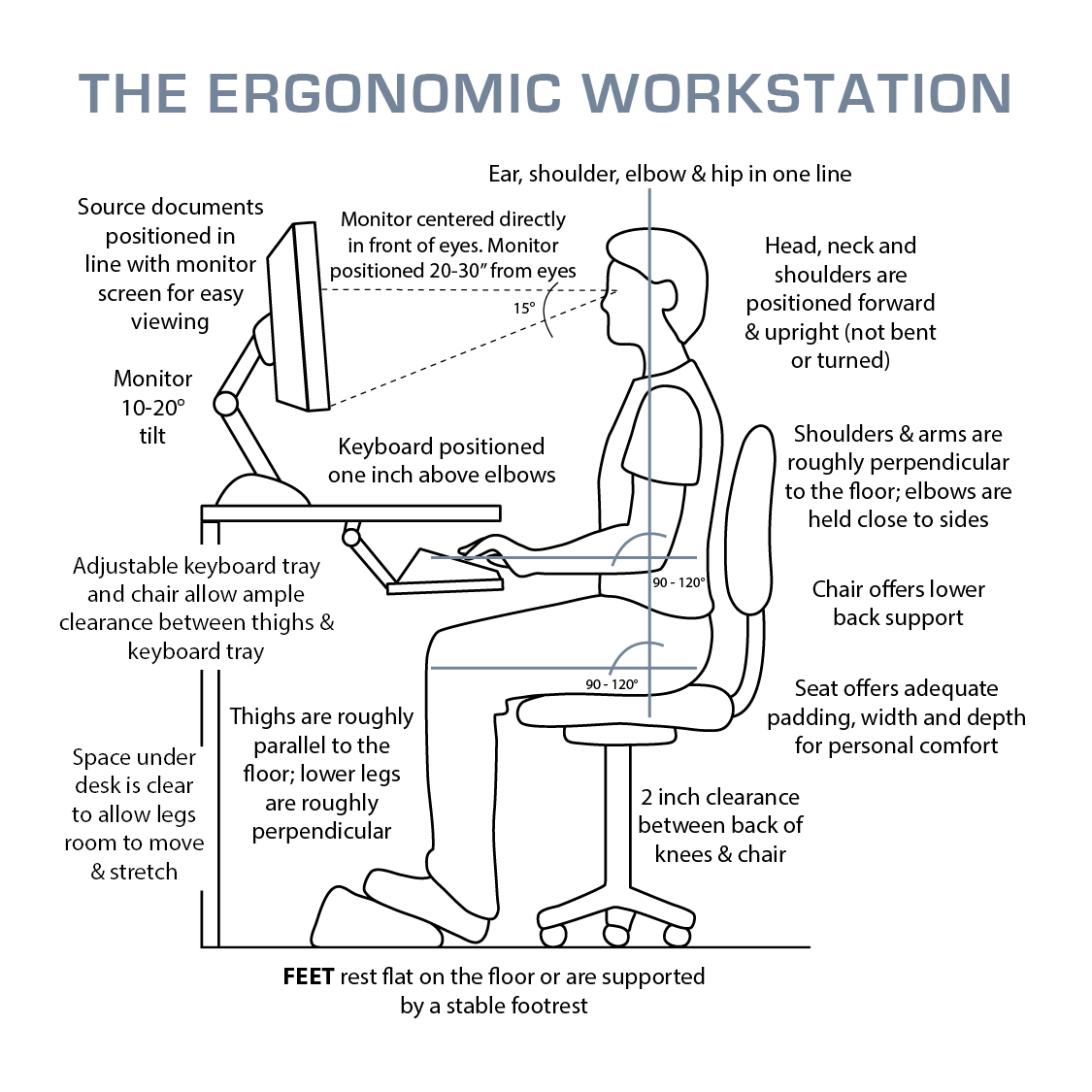
Proper body positioning in sitting is crucial to prevent discomfort, pain, and long-term musculoskeletal issues. Occupational Therapists specialize in assessing and recommending the best sitting posture to maintain overall health and well-being.
Here are some guidelines for maintaining proper body positioning while sitting:
Chair Selection: Choose an ergonomic chair with proper lumbar support, adjustable height, and armrests. Ensure that the chair allows your feet to rest flat on the floor or on a footrest.
Seat Height: Adjust your chair so that your feet are flat on the floor (or on a footrest) and your knees are at a 90-degree angle. Your thighs should be parallel to the ground.
Back Support: Position your lower back against the chair’s lumbar support or use a lumbar roll to maintain the natural curve of your spine. Avoid slouching or leaning forward.
Armrests: Adjust armrests so that your arms can comfortably rest on them with your shoulders relaxed. Avoid hunching your shoulders or keeping them raised.
Keyboard and Mouse: Keep your keyboard and mouse close enough to your body to avoid overreaching. Your wrists should be straight, and your hands should float comfortably above the keyboard and mouse.
Monitor Placement: Position your monitor at eye level, directly in front of you. Ensure that the top of the screen is at or just below eye level to prevent neck strain. Use a monitor stand or adjust the monitor’s height if needed.
Feet Placement: Keep your feet flat on the floor or on a footrest. Avoid crossing your legs or sitting on one foot, as this can lead to poor circulation and discomfort.
Posture: Sit back in the chair with your back straight and shoulders relaxed. Maintain a neutral spine position to distribute the weight evenly across your spine.
Breaks and Movement: Take short breaks every 30 minutes to stand up, stretch, and walk around. Gentle stretching exercises can help relieve muscle tension.
Eyes: Blink frequently to prevent dry eyes and use the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds to reduce eye strain.
Monitor Glare: Position your monitor to minimize glare from windows or overhead lighting. Use an anti-glare screen protector if needed.
Footrest: If your feet do not comfortably reach the floor, use a footrest to support your feet and maintain proper posture.
Remember that maintaining proper sitting posture is essential not only during work but also in various everyday activities. Occupational Therapists can provide personalized guidance and exercises to help you achieve and maintain a healthy sitting posture that supports your overall well-being.